In many people's perception, "stainless steel" is "rust-free steel", if it rusts, it must be a counterfeit product! This view is actually too one-sided. First of all, the stainless steel is "stainless", not absolute rust, but relative in standard conditions of use with good corrosion resistance, not easy to rust.
If not properly installed and maintained, or used in an environment or conditions beyond its corrosion resistance, thin-walled stainless steel water pipes will rust. Today we are together to understand the causes of corrosion and solutions for stainless steel piping applications (a).
Improper installation of pipes leads to corrosion problems
01 - Problem: Welding construction (bracket, electrical box, fire piping, etc. welding) did not protect the stainless steel piping, resulting in welding slag splash to the stainless steel piping, resulting in potential corrosion.
Solution: After the installation of stainless steel piping, the pipeline should be protected when welding operations are carried out around the pipeline to avoid welding slag splashing onto the surface of the stainless steel pipeline, leading to potential corrosion.
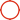
02 - Problem: The pipe is fixed using iron brackets and is not protected resulting in potential corrosion.
Solution: Galvanized iron frame can not directly contact the stainless steel pipeline, it is recommended to use stainless steel fixed bracket, such as the use of an iron bracket should be well protected.
03 - problem: contact or connection of dissimilar metal pipes without protection transition, resulting in potential corrosion (common in the old and new pipe connections, available copper and copper alloy joints for transition).
Problem: concealed buried pipes in the wall directly with bare pipes, the installation process using iron nails fixed, after the construction is not removed the iron nails, resulting in potential corrosion rust.
Solution.
Stainless steel pipe and different materials connected to the pipe, depending on the material of the pipe, some can be directly connected, some will produce electrochemical stress corrosion, and must be electro-insulated treatment before connection.
Can be directly connected to the tube.
(1) stainless steel tubes - copper tubes, copper alloy tubes with similar potential use connection no problem
(2) stainless steel tube - stainless steel plastic composite tube
(3) stainless steel tube - aluminum-plastic composite tube is a bad conductor can be used to connect
(4) stainless steel pipe - PPR, PE, PEX, PVC-U, ABS
04 - Problem: Pipe cutting burrs are not cleaned, resulting in rusting; scattered iron dust generated during construction is attached to the metal surface, which also easily causes rusting. The iron powder is brought into the pipe when cutting the pipe and enters the stopping bit during cleaning, leading to corrosion generation and further inducing pitting perforation.
Solution.
1) Use special cutter to cut the pipe.
(2) if you need to use the wheel cutting, should cut the pipe inside and outside the "burr" clean, and should be cleaned due to cutting iron powder within the pipe, in the water test pressure, the possible debris in the pipe should be discharged first.
(3) pipe and fittings should avoid contact with corrosive media, iron, soil, gravel, to prevent corrosion.
05 - problem: stainless steel bare pipe directly concealed buried (buried), the formation of giant battery corrosion and galvanic corrosion.
Concealed buried pipe precautions.
(1), buried in the soil
A, general non-corrosive land, sandy soil, loess can be directly buried, pipe base burial should be in line with construction specifications.
B, general non-corrosive soil, buried pipe through the road, river, etc. should be set up casing, casing can not be directly galvanized pipe or carbon steel pipe, if the use of steel casing, should be made in the pipe lining, lining materials for insulation and non-corrosive materials. Such as: cement mortar lining, resin type lining. Outside the casing should be made anti-corrosion, such as asphalt anti-corrosion, epoxy coal asphalt anti-corrosion, etc. Crossing casing can also choose steel cement pipe, plastic pipe, etc.
C, due to dissolved salts in the soil, acidity, water content, aeration and many other factors land can cause corrosion, generally 304 pipe can be in the chloride content of less than 200PPm, 316 pipe can be in less than 1000PPm environment without taking anti-corrosion measures, the choice of direct burial in the soil construction. When greater than the specified value, especially poor soil quality, such as: the coast has a fascinating current will cause electrochemical corrosion of the pipeline, should do anti-corrosion treatment, can be used to wrap anti-corrosion tape outside and overlap 1/2 width. Or other effective anti-corrosion treatment.
(2), buried in concrete
When buried in the concrete stainless steel thin-walled water supply pipe, the pipe is not allowed to directly with the concrete pouring into one. Certain anti-corrosion protection measures should be taken or the use of clad stainless steel pipe.
(3), buried in the wall of the floor
Indoor concealed buried pipes, should be buried in the building layer; should not be buried directly into the force structure layer, must be set through the casing. Wall buried pipes should be wrapped stainless steel pipe, the diameter of the pipe should not be greater than 25mm.
Active interface, such as: wire connection, flange, live joint is not allowed for indoor concealed buried. Indoor concealed buried pipe before burial should be fixed interface, pipe inspection water, air pressure test, the reserved interface should be temporarily blocked.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)